What is endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue grows in the wrong places, it can cause painful symptoms that can impact not only your menstrual cycle but also your daily life. Some people with endometriosis have trouble getting pregnant due to scarring and fallopian tube blockage as well. Endometriosis is a condition where tissue that is similar to the lining of your uterus grows on other parts of your body.
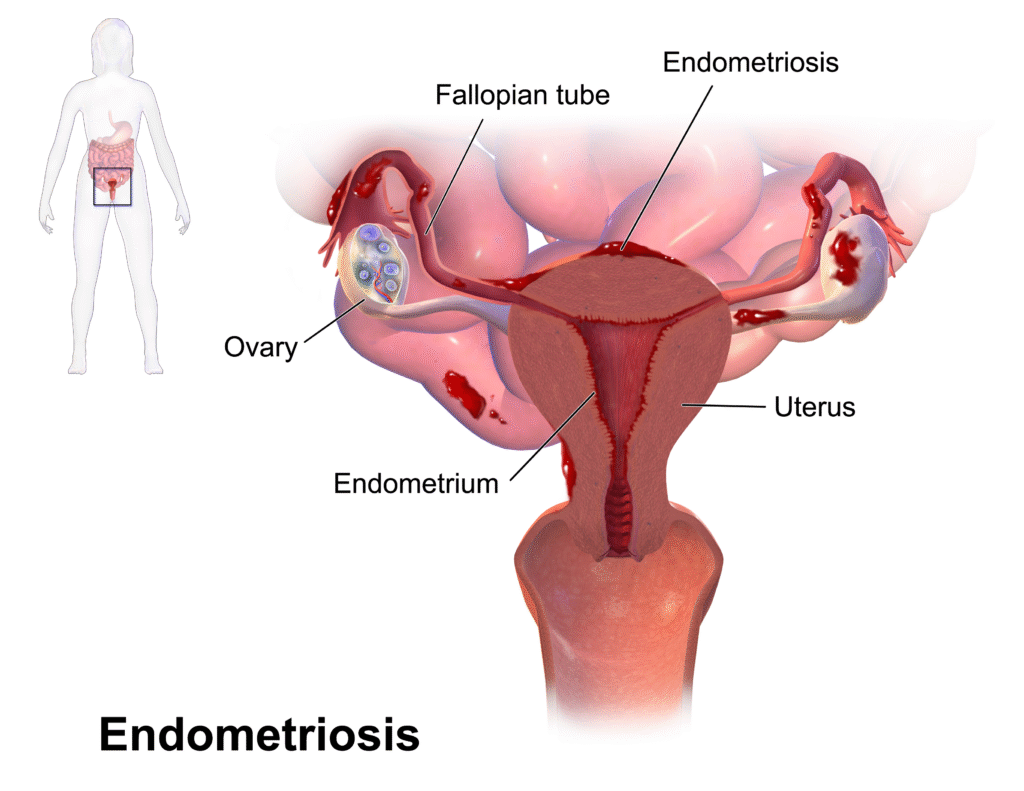
Mc place develop Endometriosis develop include in Ovaries, Peritoneum and Fallopian tube. it is common condition that affects about 1 in 10 females worldwide.
What are the symptoms of endometriosis?
There are many symptoms of endometriosis, but the most common is pelvic pain. This pain can be intense or mild. Symptoms often feel worse just before and during your period due to inflammation brought on by the hormonal changes that occur at that time.
Symptoms of endometriosis include:
Dysmenorrhea (Mc)
Vicarious menses
Cyclical symptoms related to ectopic tissue
Very painful menstrual cramps.
Abdominal pain or back pain during your period or in between periods.
Heavy bleeding during periods or spotting (light bleeding) between periods.
Pain during sex (dyspareunia).
Infertility.
What causes endometriosis?
Healthcare providers don’t know for sure what causes endometriosis. When you have endometriosis, tissue that is similar to the lining of your uterus grows in the wrong places. Researchers are looking for a connection between endometriosis and conditions like retrograde menstruation, immune system conditions and hormone disorders as possible factors that may lead to the condition.
Who can get endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a condition that most commonly impacts females between the ages of 20 and 40. It can also happen to younger people during their teenage years. Although many people find relief from endometriosis symptoms after menopause, it can still cause discomfort and pain.
What are some of the risk factors for endometriosis?
- Family history
- Menstrual cycle characteristics
- (starting period before the age of 12 years)
- Immune system disorders
- Abdominal surgery
- age 20 to 30
You can probably reduce your risk by lowering the amount of estrogen in your system.
One of the functions of estrogen is to thicken your uterus lining, or endometrium. If your estrogen level is high, your endometrium will be thicker, which can cause heavy bleeding. If you have heavy menstrual bleeding, you’re at risk for developing endometriosis.
Being in a healthy state balances hormones. To keep hormones such as estrogen at normal or lower levels, try these strategies:
Exercise regularly.
Eat whole foods and less processed foods.
Consume less alcohol.
Reduce your caffeine intake.
Talk to your doctor about your birth control medication to see if there is a type you can switch to that contains less estrogen.
How to diagnose Endometriosis ?
You’ll be asked to describe your symptoms, including where and when you feel pain.
Tests to check for clues of endometriosis include:
- Pelvic exam
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Laparoscopy
- A laparoscopy can provide information about the location, extent and size of the endometriosis growths. it is gold standard test for endometriosis.
Treatment of endometriosis
Symptomatic treatment
Pain medicines
Your health care team may recommend pain relievers that you can buy without a prescription. These medicines include the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve). They can help ease painful menstrual cramps.
Hormone therapy
Sometimes, hormone medicine help ease or get rid of endometriosis pain. The rise and fall of hormones during the menstrual cycle causes endometriosis tissue to thicken, break down and bleed. Lab-made versions of hormones may slow the growth of this tissue and prevent new tissue from forming.
Hormone therapy isn’t a permanent fix for endometriosis. The symptoms could come back after you stop treatment.
Therapies used to treat endometriosis include:
Hormonal contraceptives. Birth control pills, shots, patches and vaginal rings help control the hormones that stimulate endometriosis.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists and antagonists
Progestin therapy
Aromatase inhibitors
